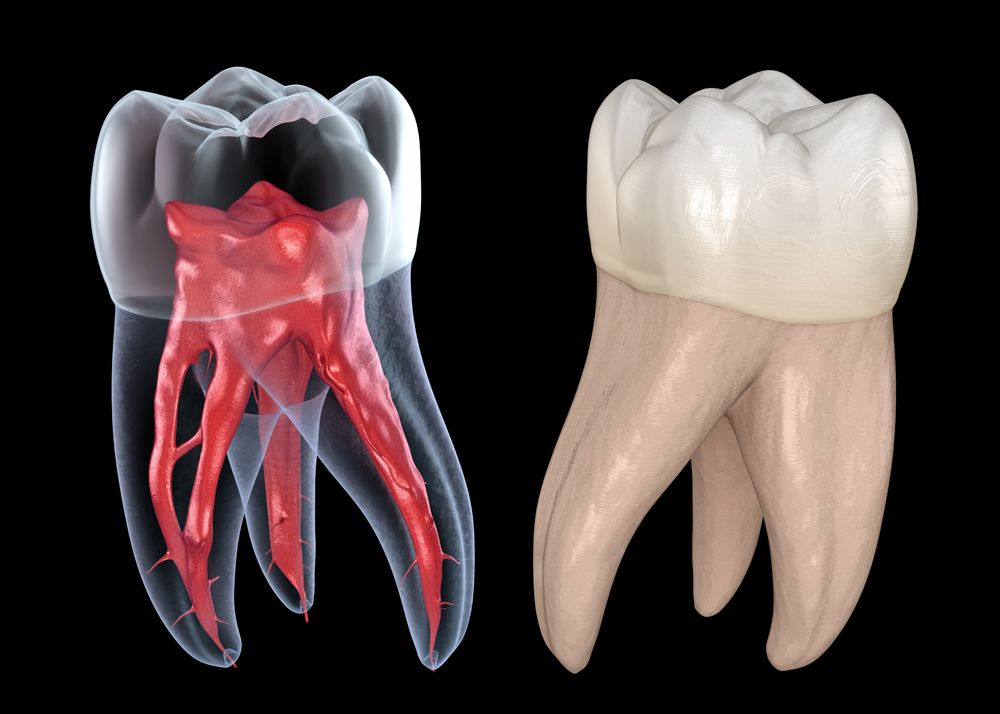
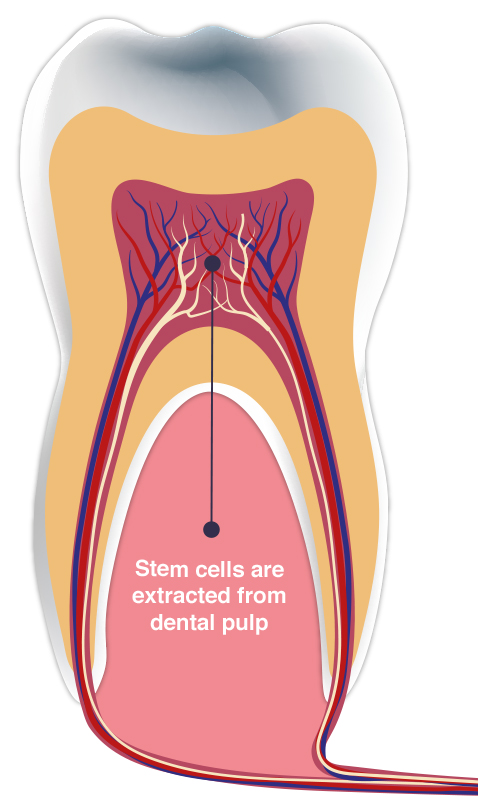
Primary contributes to symptomatic pulpitis area unit infection, inflammation and pressure changes. And symptoms area unit directly proportional to matured innervation/vital nerve fibers.
- Inflammation brings concerning tube changes (vasodilation, edema) that will increase native pressure, once the pressure crosses essential intrapolar pressure (as the pulp chamber is non-expandable) the pressure falls back on nerves thence pain is felt.
- Their area unit bound things wherever this accumulated pressure can ne’er cross essential intra pulpal pressure, eg: open sort of pulpitis, wherever the dropsy fluid merely escapes through an enormous cavity shaped because of decay.
- Inbound conditions like chronic irreversible pulpitis, there are a unit small bass forming inside the infected pulp, their area unit instances once these micro abscesses burst and coalesce. the pressure changes caused by these events will initiate the pain.
- These all-symptoms area unit extremely variable among people, individual teeth, kind (primary/permanent) and age of the teeth. individual variation is primarily owing to absolute threshold. in primary and young permanent teeth, the neural tissue isn’t significantly dense and it’s immature. thence the probabilities of symptomless progress of pulpitis area unit high in such teeth.
- Finally, another contributive issue is the speed of progress of the lesion. in cases of code or rampant decay, the destruction is very fast, which destroys nerve fibers in a very fraction of your time, going away with little or no time for symptom development.
- Once the pulpitis achieves periarticular symptom, identical principles of “pressure changes” apply. Sooner the pressure alleviated (usually sinus formation) proprietor the symptoms.
- Pulpal pathology is one of the smallest amounts explored subjects in dental medicine. Glad to examine this question. Hope I self-addressed the question a minimum of to some extent